 Writing Effective Java Tests with Assertion Libraries
Writing Effective Java Tests with Assertion Libraries
JUnit, Hamcrest, AssertJ, TestNG, and Truth
Java has several assertion libraries that can help you with testing and debugging your code. In this article, we’ll look at various assertions libraries and compare them.
Overview
Test-driven development (TDD) has gained popularity in the last few years. TDD promotes writing tests before developing a functionality, which increases requirement understanding, reduces defects, and decreases bugs in the early phase of development. We write the unit tests for each piece of code and use assertion libraries to verify the expected output.
There are multiple libraries available in the Java ecosystem, some of the popular ones are: JUnit, Hamcrest, AssertJ, TestNG, and Truth. Let’s look at each one of them:-
Junit
- Junit is the most widely used testing framework in Java.
- Junit comes bundled with many popular IDEs such as IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, NetBeans, and Visual Studio Code and build tools such as Maven, Gradle, and Ant
- Junit is the default testing module in Spring Boot Framework
- Junit serves as a foundation for developing and launching testing framework on the JVM
- Junit provides basic assertion methods.
As a developer, you should be using Junit to write and run test cases in Java most of the time. Junit has limited assertion methods which are enough for writing basic test cases. You should consider using AssertJ or Hamcrest assertion methods along with Junit framework for writing complex test case conditions.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
public class MyClassTest {
@Test
public void testAddition() {
int result = MyClass.add(2, 3);
assertEquals(5, result); // pass
assertNotEquals(0, result); // pass
assertNotNull(result); // pass
assertTrue(result > 0); // pass
}
}
TestNG
- TestNG is a testing framework inspired by JUnit and NUnit but introduces some new functionalities that make it more powerful and easier to use
- TestNG provides more advanced features than JUnit, such as data-driven testing and parallel test execution
- TestNG is designed to cover all categories of tests: unit, functional, end-to-end, integration, etc…
- TestNG is a popular library to write test cases in Selenium.
import org.testng.Assert;
public class MyClassTest {
@Test
public void testAddition() {
int result = MyClass.add(2, 3);
Assert.assertEquals(result, 5);
}
}
Hamcrest
Hamcrest is a widely used library that provides a set of matchers for testing conditions. It allows you to write more complex assertions by combining matchers using logical operators.
- Hamcrest matchers are available in several languages - Java, Python, Ruby, Obj-C, PHP, Erlang, Swift, Rust, JavaScript (JsHamcrest), JavaScript (Hamjest), GO (Gocrest), and C# (NHamcrest)
- Hamcrest can be used with JUnit (all versions) and TestNG
- Hamcrest provides the ability to write custom matchers for testing custom classes
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class MyClassTest {
@Test
public void testAddition() {
int result = MyClass.add(2, 3);
assertThat(result, equalTo(5));
}
}
AssertJ
- AssertJ is a fluent assertion Java library that provides a rich set of assertions and truly helpful error messages.
- AssertJ is composed of several modules:-
- Core module to provide assertions for JDK types (String, Iterable, Stream, Path, File, Map…)
- Guava module to provide assertions for Guava types (Multimap, Optional…)
- Joda Time module to provide assertions for Joda Time types (DateTime, LocalDateTime)
- Neo4J module to provide assertions for Neo4J types (Path, Node, Relationship…)
- DB module to provide assertions for relational database types (Table, Row, Column…)
- Swing module provides a simple and intuitive API for functional testing of Swing user interfaces
- AssertJ has a very good starter guide and documentation to follow:- https://assertj.github.io/doc/
- AssertJ assertions can be used with Junit framework to test complex conditions.
- AssertJ is designed to be super easy within your favorite IDE. Type
assertThatfollowed by the object under test and a dot … and any Java IDE code completion will show you all available assertions like this:-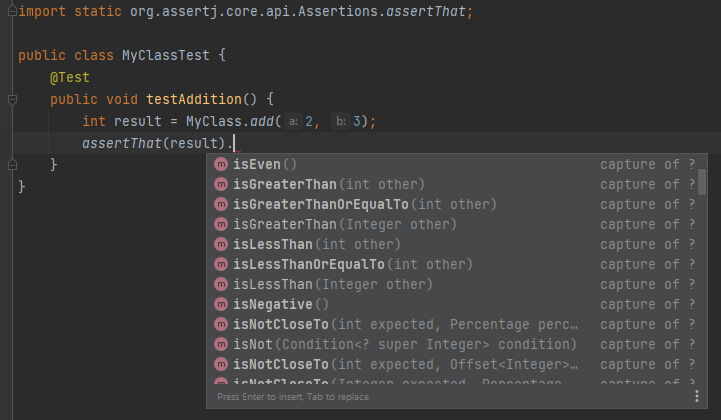
- AssertJ assertThat can be used like this:-
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat; public class MyClassTest { @Test public void testAddition() { int result = MyClass.add(2, 3); assertThat(result).isEqualTo(5); // pass assertThat(result).isNotZero(); // pass assertThat(result).isPositive(); // pass assertThat(result).isOdd(); // pass assertThat(result).isLessThan(6); // pass assertThat(result).isGreaterThan(0); // pass } } - The
Assertionsclass is the only class you need to start using AssertJ, it provides all the methods you need. One Assertions static import to rule them all …… or many if you prefer:import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat; // main one import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.atIndex; // for List assertions import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.entry; // for Map assertions import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.tuple; // when extracting several properties at once import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.fail; // use when writing exception tests import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.failBecauseExceptionWasNotThrown; // idem import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.filter; // for Iterable/Array assertions import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.offset; // for floating number assertions import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.anyOf; // use with Condition import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.contentOf; // use with File assertions
Truth
- Truth is an assertion library developed by Google’s Guava team. It provides fluent assertions for Java and Android.
- Truth is used in the majority of the tests in Google’s codebase.
- Truth is inspired by AssertJ and you will find many similarities between Truth and AsserJ
- Truth provides fewer assertions as compared to AssertJ
- Similar to AsserJ, If you’re using an IDE with autocompletion, it will suggest a list of assertions you can make about the given type.
import static com.google.common.truth.Truth.assertThat;
public class MyClassTest {
@Test
public void testAddition() {
int result = MyClass.add(2, 3);
assertThat(result).isEqualTo(5);
}
}
Comparison
Let’s compare all the Java assertion libraries based on their usage, type of assertions available, customization support, etc.
Junit vs TestNG vs Hamcrest vs AssertJ vs Truth
| Comparison | Junit | TestNG | Hamcrest | AssertJ | Truth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available | since 2000 | since 2006 | since 2006 | since 2010 | since 2011 |
| Website | junit.org | testng.org | hamcrest.org | assertj.github.io | truth.dev |
| Source Code | junit-team/junit5 | cbeust/testng | hamcrest/JavaHamcrest | assertj/assertj | google/truth |
| Usage | assertMethod (expected, actual) | Assert.method (actual, expected) | assertThat(actual, method(expected)) | assertThat(actual) .method(expected) | assertThat (actual) .method(expected) |
| Soft Assertions* | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Boolean checks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Number checks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| String checks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Null checks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Array checks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Map checks | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Date checks | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Exception checks | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Custom Message | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Create Own Assertion | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
*Soft assertions do not throw an exception automatically on assertion failure but at the very end of the scenario and then show all failures within the scenario, not just the first one. Hard assertions throw an error during execution when the condition is not being met so test cases are marked as failed.
Hamcrest vs AssertJ
Hamcrest and AssertJ are the two most popular open-source Java assertion libraries available in the market today. Let’s compare them:-
| Comparison | Hamcrest | AssertJ |
|---|---|---|
| First Release | Back in March, 2006 | Back in September, 2010 |
| Website | hamcrest.org | assertj.github.io |
| Source Code | hamcrest/JavaHamcrest | assertj/assertj |
| Assertions | Matchers | Fluent assertions |
| Contributors | Less number of contributors and less commits | More number of contributors with regular commits |
| Popularity | Declining | Increasing |
| Release Frequecy | Latest version released 4 years ago | Frequent releases every year and month |
Hamcrest is still the most used library and is available in many different languages other than Java. On the other hand, AssertJ is gaining more popularity over the past few years and matches up with Hamcrest as per google trends.
Conclusion
JUnit and TestNG frameworks are used to automate the testing process, which also comes with basic assertions. Junit is more popular as compared to TestNG and enough to use for basic Projects. Hamcrest and AssertJ are used along with Junit to write more complex and readable assertions. Truth is similar to AssertJ but comparatively less popular and mostly used in Google’s codebase. Ultimately, the choice of assertion library depends on your personal preference and the needs of your project.
